Climate Change
In response to the impact of climate change issues, the Company follows the guidelines provided by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) proposed by the International Financial Stability Board (FSB). Analysis of the impacts of climate change by the task force. In addition to analyzing the risks brought by climate change and the Company’s countermeasures, it also proposed new products and new market opportunities that the Company can grasp under the climate change in the future. At the same time, Chroma has set the goal of “net-zero emissions at office sites by 2030 and net-zero emissions across all facilities by 2050.” The Company is working toward this goal by conducting inventories of production and office environments, improving manufacturing processes, and promoting green product design, gradually transitioning from low-carbon practices to net-zero emissions. The four core pillars outlined in the TCFD framework are explained individually as follows.
Governance
1-1 The Board of Directors is the highest governance body of the Company for the management of climate-related risks and opportunities. The Board of Directors is responsible for overseeing and reviewing the development of strategies and formulation of policies. This includes identifying risks and formulating strategies across various aspects of the Company to ensure that Chroma can mitigate future impacts and capitalize on potential opportunities.
1-2 Members of the Board of Directors have a thorough understanding of the importance and impact of climate change. Climate-related issues have already been incorporated into major investment decisions. For example, topics such as carbon management and the use of energy and resources in response to climate change risks are carefully reviewed and discussed to ensure informed decision-making.
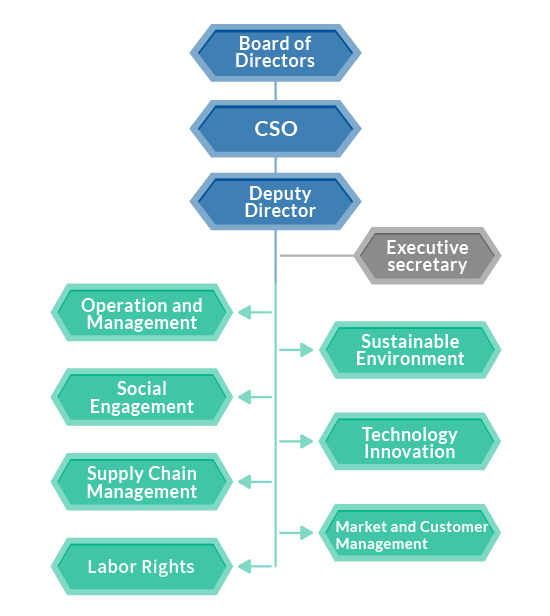
Climate change Governance and Management Framework
Chroma established the Chroma ESG Working Group in 2022 as authorized by the Board of Directors. The CFO serves as the Chief Sustainability Officer (CSO), reporting directly to the Chairman of the Board.
Given the broad scope of climate change issues, the Chroma ESG Working Group selected representatives from various departments based on functional units to participate in assessing risks and opportunities and to discuss and decide response strategies. Departments participating in the assessment of climate change issues include: Innovation and Research, Operations, Production, Procurement, Finance, Environmental Health and Safety (EHS), and Human Resources. Discussions involve departmental managers and above, who assist the Company in determination of the potential impact of climate change on future market opportunities and business operations in terms of scale, frequency, and intensity. Focus was on how to respond to potential risks and adopt appropriate mitigation measures while maintaining normal business operations.
In October 2022, following thorough discussion by relevant department heads, the ESG Working Group completed its initial assessment of climate change risks and opportunities. Climate risks and opportunities were identified and addressed through tailored action plans. After follow-up and evaluation by each responsible department, results were reported back through the administrative management system. Departments set KPIs based on their respective tasks. Moving forward, team members will hold regular monthly progress review meetings to ensure that all KPIs and work items are met. Board of Directors member David Huang oversees the Company’s climate change strategies and targets, and reports on sustainability operations and outcomes to the Board twice a year.
Strategy
2-1 The ESG Working Group evaluated the 17 climate-related risks and 20 climate-related opportunities outlined in the TCFD framework based on Chroma’s core measurement business and future market development. These risks were assessed in terms of their likelihood and urgency, categorized by short-, medium-, and long-term timeframes. The team conducted discussions and prioritization to develop a climate risk matrix.
Identification of Climate Change-Related Risks and Response Measures
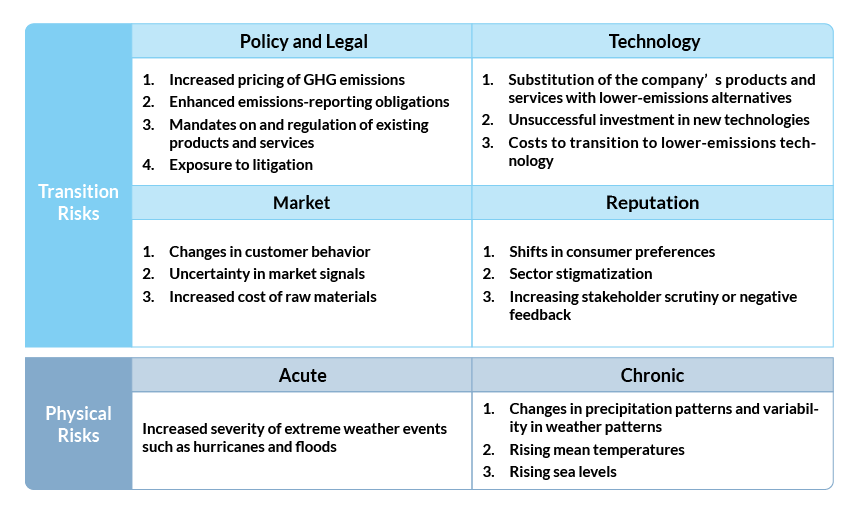
We assessed the potential financial impacts of the top four transition risks and one physical risk as follows:
Transition Risks
The cost of raw materials increased
Impact to Chroma
Because climate change has caused a shortage in the supply of raw materials, the demand for raw materials has exceeded the supply, which has led to an increase in procurement costs. This ultimately leads to an increase in manufacturing costs.
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
(1) The raw material items that may be affected and the extent of the impact.
(2) Products and scope of impact.
(3) The starting time shall be affected.
Countermeasure
- R&D : Improve the use of shared materials, modularize products, design environmentally friendly materials, recyclable materials, and design energy-saving products and machines.
- Procurement : Centralized procurement: identification of green supply chains and requiring the top five suppliers by annual transaction amount to implement carbon reduction measures. Cardboard box and wooden pallet recycling: reused internally or returned to suppliers for“ repeated use”. FSC certification: carton suppliers are encouraged to obtain FSC registration. Sustainable production practices: manufacturability planning, automated production, process improvement, and smart manufacturing.
Transition Risks
Low-carbon technology transformation
Impact to Chroma
The world has set a net-zero emissions target. After COP27, it is expected that the world will reach its carbon peak in 2025. Subsequently, the requirements for carbon reduction will become increasingly stringent, forcing the Company to adopt more low-carbon technology transformation developments, and may consider capital expenditures or overall improvements in technology, leading to higher costs.
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
(1) The downstream fields are impacted.
(2) Cost of introducing low-carbon technology (capital expenditure).
(3) The overall cost increased due to the low-carbon technology (the increase in cost per unit)
Countermeasure
- R&D: Assess suitable low-carbon technologies.
Physical risk (Immediate)
Extreme weather events such as hurricanes and floods
Impact to Chroma
Extreme weather increases the probability of hurricanes or heavy rains/floods, which may cause flooding in the factory area or nearby communities. After assessment, it was found that the factory site of the Guishan Plant of Chroma is located at a higher altitude, and the factory itself should not be affected too much, but the factory’s external transportation may be hindered, resulting in reduced revenue or increased costs.
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
(1) Ongoing operational planning costs
(2) Cost of alternatives
Countermeasure
- Environmental safety: Assess the possible level of impact and formulate corresponding emergency response measures.
Transition Risks
The Company’s existing products and services are replaced by low-carbon products
Impact to Chroma
If the Company does not grasp the technology for relevant low-carbon products, or if competitors’ low-carbon products are launched first, the Company’s market share may be eroded in the future, resulting in reduced revenue.
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
(1) Possible impact
(2) Cost of alternatives
Countermeasure
- R&D: Introduce new-generation green energy technology, lead market demand, and expand market share.
- Market: Through brand projects, we collaborate with well-known laboratories to strive to become a green product specification setter.
Transition Risks
Pricing of GHG emissions
Impact to Chroma
Under the broader goal of net zero emissions, GHG emissions will be influenced by policies, including carbon pricing. Although the manufacturing process of Chroma is low-carbon emission, if GHG emission pricing increases, it will have a certain impact on the overall cost of the Company’s products, leading to an increase in overall costs.
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
(1) Carbon pricing cost
(2) Cost of alternatives
Countermeasure
- We are currently actively planning internal carbon pricing and will make further plans after national policies are confirmed.
Identification of Climate Change-Related Opportunities and Response Measures
We assessed the potential financial impacts of the first three transition opportunities as follows:
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
Forecast the speed of new product launch by downstream markets
Countermeasure
- Market: Focus on understanding product demand in new markets by re-evaluating and collecting information on required materials and equipment suppliers
(1) Dedicated personnel are assigned to conduct market analysis for new markets
(2) Product managers in each business unit gain a precise understanding of customer needs
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
Average revenue of existing/new customers
Countermeasure
- Recruit R&D personnel with relevant technologies.
- Formulate marketing strategies and after-sales service plans for new markets.
(1) Cultivate/recruit marketing talent for new markets.
(2) Plan a comprehensive after-sales service system to meet the needs of new markets. - Participate in communication protocol development organizations to understand new generation communication standards and set future technology development goals.
- Improve the accuracy and coverage of SI analysis simulation to reduce the development and testing time of practical measurement systems
- Introduce academic consultants to accelerate the learning curve.
- Based on the Company’s existing products and technologies as a stepping stone, we try to enter new markets that the Company has never touched before, such as green energy industry, electric vehicles, semiconductors, etc., and understand customers’ testing pain points.
Subsequent financial calculation requirements
Number of new customers, Number of new products
Countermeasure
- R&D: Introduce new-generation green energy technology, lead market demand, and expand market share.
- Evaluate the development needs of both standard and customized products, and formulate R&D strategies in response to market demand
Risk Management
3-1 In order to assess climate-related risks, Chroma’s ESG Working Group referred to the TCFD Guidelines, the Global Risk Report, and the Taiwan Climate Change Research Report for 2050. Taking into consideration the actual conditions of its operating markets, the team conducted a comprehensive evaluation of both transition risks and physical risks as outlined in the TCFD framework.
3-2 After the first TCFD report was released by the ESG Working Group in 2022, the Company adopted an annual risk assessment approach to manage the currently identified climate-related risks and opportunities. Following reporting to the Board of Directors, the results will be disclosed in the corporate sustainability report.
3-3 Response measures have been developed for four major transition risks, including rising raw material costs, the transition to low-carbon technologies, the replacement of existing products and services with low-carbon alternatives, and GHG emissions, as well as one significant physical risk, which is extreme weather events such as hurricanes and floods.
Each risk is assessed based on its urgency (short, medium, or long term), likelihood of occurrence, and potential negative impact (evaluated on a five-level scale: high, medium-high, medium, medium-low, low). The ESG Working Group takes actual customer circumstances into account and, through internal control review processes, determines the severity and prioritization of climate-related risks.
Following the first publication of Chroma’s TCFD report in 2022, the Company continues to conduct risk assessments annually to manage currently identified climate-related risks and opportunities. Climate change risks and opportunities are treated as key management issues. After reporting to the Board of Directors, the results are disclosed in the Corporate Sustainability Report.
Chroma ATE completed the ISO 14064-1:2018 greenhouse gas inventory in 2021 and began implementing TCFD-aligned financial assessments for climate change in 2022. Following the environmental risk assessments, Chroma proactively sets increasingly science-based targets for emissions reduction.
Beginning in 2023, all operational risk assessments have been integrated, including climate risk assessments within the broader scope of environmental risks. Concrete risk management actions are implemented across departments. Annual risk assessments are conducted to ensure a thorough understanding of evolving risks and to develop corresponding reduction and management measures.
Metrics and Targets
4-1 Based on the above strategies and risk management processes, the ESG team has identified corresponding measures that require immediate action. Each year, we will implement a quantitative tracking and management mechanism for each of the above indicators.
4-2 For GHG emissions, we have set the goal of“ achieving net-zero emissions at office sites by 2030 and across all facilities by 2050”. The Company completed third-party verification of GHG emissions in accordance with ISO 14064-1 in 2021 (which also serves as the base year), and will continue to collect carbon emission-related data in accordance with the established methods to ensure the accuracy of GHG emissions. We regularly disclose data related to GHG emissions in our sustainability reports and communicate this information with stakeholders.
4-3 In light of the global wave of net zero emissions and the carbon border mechanisms in Europe and the US, the transition to net zero is no longer an environmental issue; it is an economic issue critical to the international competitiveness
of companies. The industry continues to promote the deployment of green energy, bringing business opportunities in smart cities, smart transportation, smart grids, and energy storage. Chroma offers testing solutions across various green energy technology sectors and has received repeated recognition from leading international manufacturers. Leveraging its innovation in measurement technology, the Company has developed a range of energy recovery testing solutions to meet global green initiatives. These solutions not only help customers save on high electricity costs but, more importantly, reduce carbon emissions, thereby driving and accelerating the industry’s transition to net zero. Looking ahead, Chroma will continue to focus on developing low-carbon products that enhance user benefits and provide customers with a broader range of solutions. In 2023, following the release of Chroma’s first Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) report, the Company established management targets, formulated response strategies and action plans, and began systematically disclosing the progress and outcomes of these climate-related efforts.
4-4 At the end of 2024, Chroma signed a green power wheeling agreement with a renewable energy provider. The agreement is expected to supply 900 thousand kWh of green electricity in the first year, accounting for 5% of the Company’s total electricity consumption. Starting in 2025, Chroma plans to increase the proportion of green electricity by an average of 5% each year, aiming to achieve RE30 by 2030.
Based on the above strategies and risk management process, the ESG Working Group has identified corresponding actions requiring immediate implementation, along with the indicators to be tracked moving forward:
Response Measures
- R&D: Increase use of standardized components, modular product design, use of eco-friendly and recyclable materials, and energy-efficient machine design.
- Procurement: Centralized purchasing, sourcing from green supply chains, and requiring the top five suppliers by annual transaction value to reduce carbon emissions.
- Manufacturing: Design for manufacturability and automated production.
Indicators & Targets
(1) Track and increase the share of energy-efficient products.
(2) Conduct environmental risk assessments for suppliers and set carbon reduction targets for the supply chain.
Starting in 2023, we established a quantitative tracking and management mechanism for each of the above indicators.
Regarding greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, our long-term target is net zero by 2050. With third-party verification under ISO 14064-1:2018 for our GHG emissions, we will continue collecting emissions data according to established methodologies to ensure data accuracy. GHG-related information will be regularly disclosed in the Sustainability Report as part of our stakeholder communication.
Given the global momentum toward net zero and the introduction of carbon border adjustment mechanisms in Europe and the U.S., the transition to net zero is no longer solely an environmental issue but also a matter of economic competitiveness. As industries push forward with green energy infrastructure, opportunities are also emerging in smart cities, smart transportation, smart grids, and energy storage.
Chroma offers testing solutions across these green technology sectors and has earned recognition from major international clients. Leveraging innovation in measurement technologies, we are developing multiple energy recovery testing solutions to support global green initiatives—helping customers reduce electricity costs while significantly cutting carbon emissions. These efforts drive and accelerate industry-wide net-zero transformation.
Looking ahead, we will continue to develop low-carbon products that enhance end-user benefits, positioning ourselves as a carbon handprint contributor within the supply chain and offering even more solutions to our customers.

